- por burbujeo de presión directa
- por burbujeo con cámara de vacío
- por detección de halógenos
- por cambio de presión
- por espectrómetro de helio y sonda, trazador y sonda y mediante campana
- por sonda de detección de la conductividad térmica
- por ultrasonidos
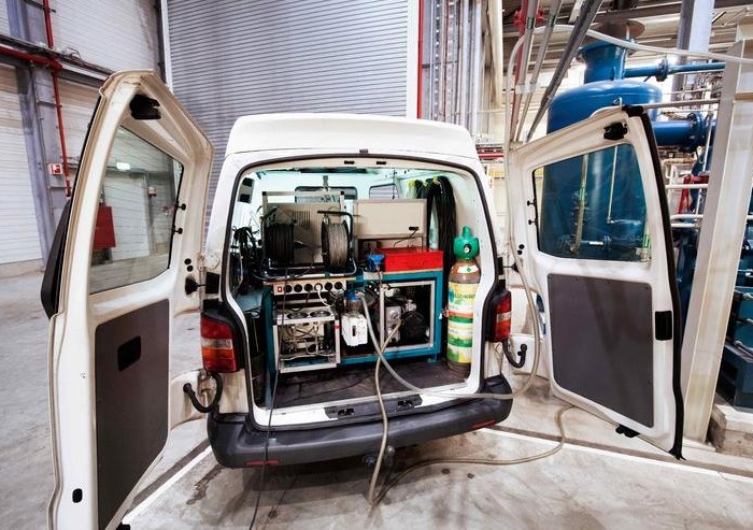
- En primer lugar, realizar una prueba de fugas sobre un componente o un sistema antes de ponerlo en servicio tiene muchos beneficios. Por ejemplo, una prueba de fugas con helio en un intercambiador de calor permite verificar la tasa de fugas en las soldaduras de la placa de tubos, así como saber si hay fugas en los propios tubos. Otro ejemplo de este tipo sería realizar una prueba de fugas en vacío en la base de un tanque.
- En segundo lugar, si se sospecha que un sistema podría tener una fuga, alguno de los métodos de prueba de fugas puede ayudar a establecer su posición para poder repararla.
Pruebas de fugas por burbujeo
Las pruebas de fugas por burbujeo se utilizan para detectar fugas en muchos componentes diferentes. Las dos técnicas más habituales de pruebas de burbujeo son la de presión directa y la de cámara de vacío. La técnica de presión directa consiste en presurizar un componente con un gas para después o bien sumergirlo en una solución, o bien aplicar una solución al exterior del componente. Si hay fugas, el gas escapará a través de la solución y formará burbujas en la superficie. La técnica de la cámara de vacío se efectúa en piezas que no pueden presurizarse de forma directa o cuando no es posible acceder a ambos lados de un componente. Esta prueba se realiza aplicando una solución a una zona de una superficie que actúe como barrera de presión y creando un diferencial de presión en ella, lo que provoca que se formen burbujas a medida que el gas que fuga, por ejemplo el aire atmosférico, atraviesa la solución.
Pruebas de fugas por burbujeo
DESCARGAR VERSIÓN EN PDFPruebas por cambios de presión
Pruebas por cambios de presión
DESCARGAR VERSIÓN EN PDFPruebas por detección de halógenos
La detección de halógenos es un tipo de prueba de fugas en la que se utiliza un gas trazador y una sonda para detectar la presencia de halógenos. Detectar halógenos a través de una barrera de presión indicaría la presencia de una fuga.
Pruebas por detección de halógenos
DESCARGAR VERSIÓN EN PDFPruebas de fugas por burbujeo
Las pruebas de fugas por burbujeo se utilizan para detectar fugas en muchos componentes diferentes. Las dos técnicas más habituales de pruebas de burbujeo son la de presión directa y la de cámara de vacío. La técnica de presión directa consiste en presurizar un componente con un gas para después o bien sumergirlo en una solución, o bien aplicar una solución al exterior del componente. Si hay fugas, el gas escapará a través de la solución y formará burbujas en la superficie. La técnica de la cámara de vacío se efectúa en piezas que no pueden presurizarse de forma directa o cuando no es posible acceder a ambos lados de un componente. Esta prueba se realiza aplicando una solución a una zona de una superficie que actúe como barrera de presión y creando un diferencial de presión en ella, lo que provoca que se formen burbujas a medida que el gas que fuga, por ejemplo el aire atmosférico, atraviesa la solución.
Pruebas de fugas por burbujeo
DESCARGAR VERSIÓN EN PDFEspectrometría de masas - Pruebas de fugas con helio
Las pruebas de fugas con helio por espectrometría de masas permiten detectar fugas muy pequeñas a través de una barrera de presión. En estas pruebas se utiliza un espectrómetro de masas calibrado para detectar la presencia de moléculas de helio. Las moléculas de helio son muy pequeñas, por lo que el uso de helio como gas trazador permite localizar pequeñas fugas que no son detectables con otros tipos de pruebas de fugas. Hay tres maneras de realizar estas pruebas: - Técnica de sonda de detección - Técnica de sonda trazadora - Técnica de campana En la técnica de sonda de detección, el componente se presuriza con gas helio y, a continuación, se escanea con la sonda para comprobar si hay presencia de helio. En caso de detectarse, esto aparece indicado en el espectrómetro de masas, que se monitoriza para verificar la presencia de fugas. En la técnica de sonda trazadora, se hace el vacío en el componente, que se conecta al espectrómetro de masas. A continuación, se "rocía" helio alrededor del componente en cuestión con la sonda trazadora. Si hay una fuga, el helio se introducirá en el interior de la pieza a causa de la diferencia de presión. La presencia de helio aparece indicada en el espectrómetro de masas, que se monitoriza para verificar si hay fugas. En la técnica de campana, se hace el vacío en el componente y se conecta al espectrómetro de masas. A continuación, se coloca una “campana” o "envoltorio" alrededor de la parte del componente que se desea probar, como por ejemplo la placa de tubos de un intercambiador de calor. Posteriormente, la campana, que normalmente es un material plástico o una bolsa, se llena con helio para probar una zona grande de una sola vez. Si hay una fuga, el helio se introducirá en el interior de la pieza a causa de la diferencia de presión. En caso de detectarse, la presencia de helio aparece indicada en el espectrómetro de masas, que se monitoriza para verificar si hay fugas.